Recently, the team of Ninghua Tan/Zhe Wang from the School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy published their research results in ACS Central Science and Drug Discovery Today, the leading journals in science and pharmacy.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is highly malignant, lacks effective targeted therapies, has limited efficacy of chemotherapy and is easily resistant to drugs, and is in urgent need of new mechanism drugs. In this study, based on the strategy of biofunction-directed isolation and molecular network visualization, we obtained 24 series of RALs-like compounds from the endophytic fungus Asteraceae, a traditional Chinese medicine, and found that Pochonin D (PoD), a natural copper ion carrier, can inhibit the enzymatic activity of PRDX1 by covalently binding to its Cys173 site, promote intracellular copper ion accumulation and ROS generation, and induce copper death to exert anti TNBC activity. This study is the first to identify PRDX1 as a key target of copper death, revealing its new mechanism of regulating copper metabolism and oxidative stress, providing a novel therapeutic strategy targeting copper death for TNBC and promoting the research and development of related drugs. The related work is entitled “Discovery of natural resorcylic acid lactones as novel potent copper ionophores covalently targeting PRDX1 to induce cuproptosis for triple-negative breast cancer therapy” was published in ACS Central Science. Our postdoctoral fellows, Feng Li and Wu Tizhi, and 2022 master's student, Guo Xinrui, are the co-first authors of this paper, and Prof. Tan Ninghua, Associate Prof. Wang Zhe and Prof. Bian Jinlei are the co-corresponding authors, with our university as the only corresponding organization.
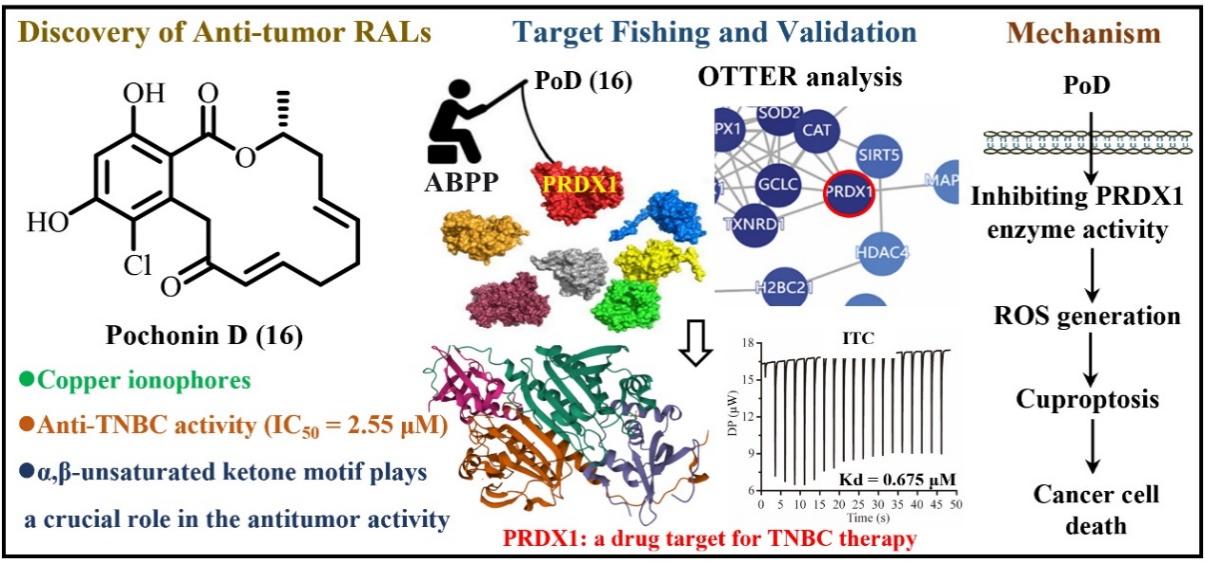
Schematic of ACS Central Science study results
In recent years, the team has focused on the discovery and target mechanism of active natural products in cyclic peptide-containing traditional Chinese medicine and its microbial resources, and systematically carried out the related work of “Discovering novel active natural products, exploring target mechanism and developing new target drug candidate molecules”, and achieved a series of research results. For the first time, the team discovered that dCTP pyrophosphatase 1 (DCTPP1) plays an anti-tumor role by regulating energy metabolism, and suggested that it could be a new target for immunological anti-cancer (Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2024). Based on the above research foundation, the team was invited to review the research progress of DCTPP1, including its structural features, biological functions and small molecule inhibitors, and also to explore its role in tumor development and target durability, and to propose its application as a small molecule interventional target, so as to provide references for the subsequent development of related drugs. The related work was published in Drug Discovery Today under the title of “DCTPP1: a promising target in cancer therapy and prognosis through nucleotide metabolism”. Today. Dr. Xuan Liu, a doctoral student of School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy, was the first author, and Associate Professor Zhe Wang and Postdoctoral Fellow Li Feng were the co-corresponding authors.
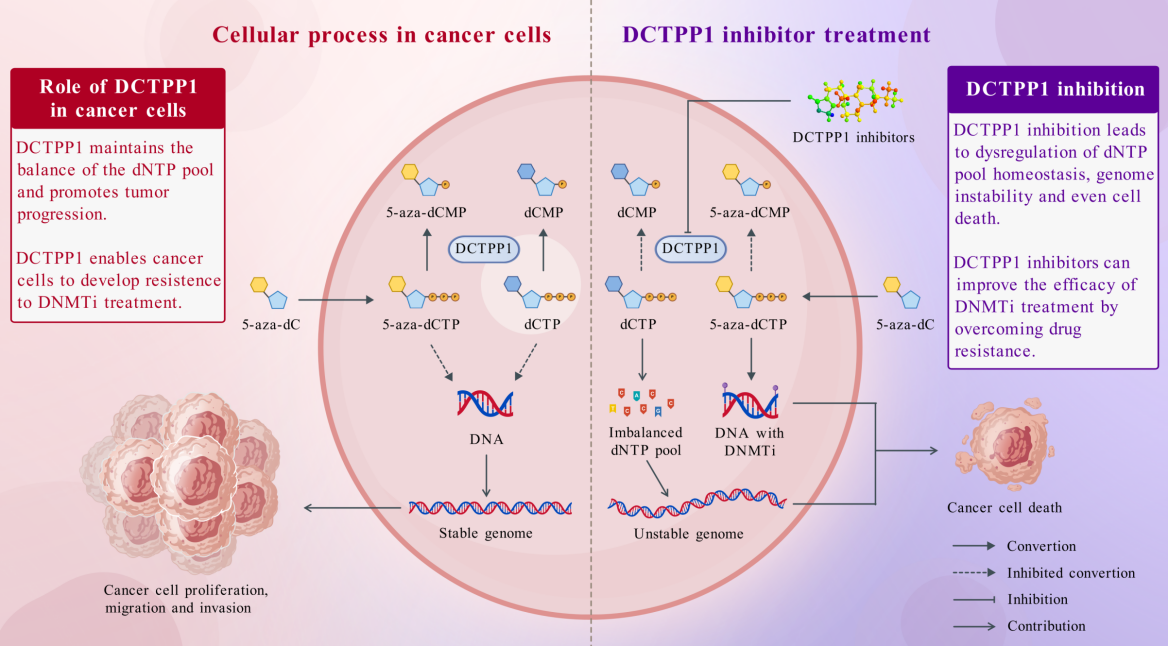
DCTPP1 function and its inhibitor
The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Upper-level Project (No. 32470426, No. 32070387, No. 32070356) and Youth Project (No. 32300338), the Excellence Postdoctoral Program of Jiangsu Province (2023ZB126), and the Open Subjects of the National Key Laboratory of Multi-targeted Natural Medicines ( SKLNMZZ2024JS10) were funded.
Article link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscentsci.4c02188
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104348
